When it comes to the world of science, discoveries and breakthroughs are made every day. To help you keep up with them, The Battalion compiles a few of the most compelling scientific stories from this past week.
Biology: A newly discovered network of fluid-filled channels in the human body may be a previously-unknown organ
Hidden beneath the top layer of a human’s skin, a new study discovered what might be the body’s biggest organ. The organ, known as the interstitium, is widespread, fluid-filled spaces within and between tissues all over the body. The scientists discovered the channels using a powerful microscope with a technique called “confocal laser endomicroscopy” to look at healthy tissue samples from human bile ducts.
The study also said the interstitium may play a role in helping cancer cells spread around the body. When cancer spreads from the tumor, it travels through the bloodstream or the lymph system. Since these interstitium spaces might act as opening, these areas could be a place to assess the body for cancer cells. The researchers also found these spaces are where the pigments of tattoos reside, and the space the tip of the needle goes in when a person take part in acupuncture.
Psychology: Brain activity study links social anxiety to a preoccupation with making errors
A new study suggests social anxiety is related to a preoccupation with making mistakes. The research comes from monitoring brain activity in children and understanding the neurological mechanisms in the symptoms in social anxiety. Taking over 100 12-year-old children who showed signs of behavioral inhibition, the researchers monitored the electrical brain activity as they completed a psychological test which studied the children’s ability to focus on information while ignoring distractions.
Looking at the post-error response times, a particular pattern of brain activity known as Error-Related Negativity linked social anxiety and hypersensitivity towards errors when under social observation. While the study isn’t significantly related to generalized anxiety, the researchers see that these measures could index a neurobehavioral mechanism linking behavioral inhibition and symptoms and diagnosis of social anxiety.
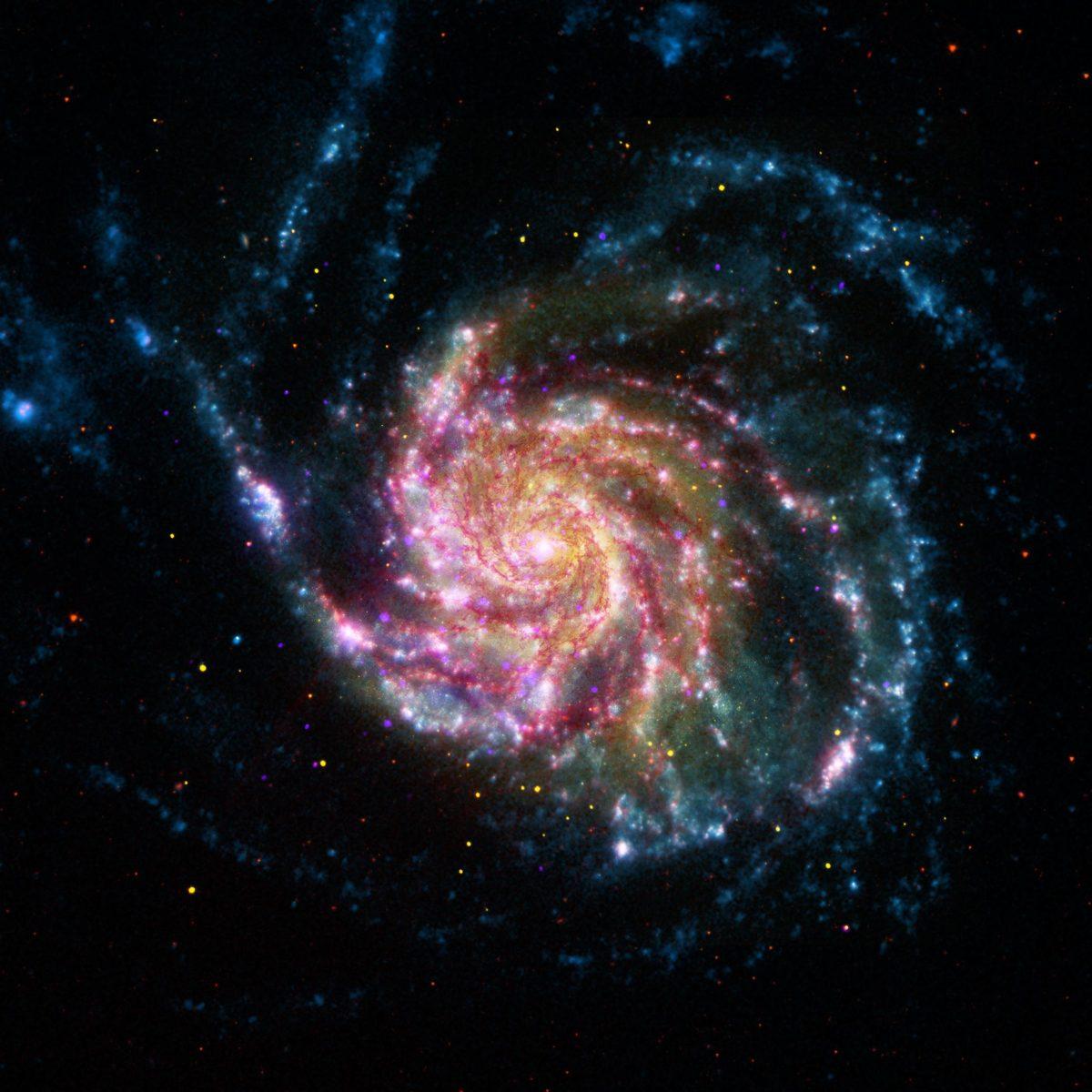
Astronomy: Researchers discover a galaxy without dark matter
A newly discovered galaxy, NGC1052-DF2, potentially seems to have little to no dark matter at all. The research found the galaxy is about 65 million light years away from Earth and holds stars with about 200 million times the mass of the Sun, but is missing about 60 billion Suns’ mass worth of dark matter.
Dark matter is an unidentified invisible substance which makes up most of the matter in the universe. Its existence is generally stated to be the explanation as to how stars swirl around galaxies and how galaxies move within clusters in the universe. By using several telescopes, the researchers studied 10 clusters of stars in the galaxy and measured their velocities. Since the clusters were moving slower than they should in a galaxy with the amount of mass present, it indicates a dark matter-free area. Further research looks to understand how the galaxy formed this way to help understanding of the properties of dark matter in general.
This week in science
March 28, 2018
0
Donate to The Battalion
$2790
$5000
Contributed
Our Goal
Your donation will support the student journalists of Texas A&M University - College Station. Your contribution will allow us to purchase equipment and cover our annual website hosting costs, in addition to paying freelance staffers for their work, travel costs for coverage and more!
More to Discover